Communication
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications.[27] Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit 22,300 miles (35,900 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently.
The radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications satellites is to relay the signal around the curve of the Earth allowing communication between widely separated geographical points.[28] Communications satellites use a wide range of radio and microwave frequencies. To avoid signal interference, international organizations have regulations for which frequency ranges or "bands" certain organizations are allowed to use. This allocation of bands minimizes the risk of signal interference.[29]Spy satellites
When an Earth observation satellite or a communications satellite is deployed for military or intelligence purposes, it is known as a spy satellite or reconnaissance satellite.
Its uses include early missile warning, nuclear explosion detection, electronic reconnaissance, and optical or radar imaging surveillance.
Navigational satellites are satellites that use radio time signals transmitted to enable mobile receivers on the ground to determine their exact location. The relatively clear line of sight between the satellites and receivers on the ground, combined with ever-improving electronics, allows satellite navigation systems to measure location to accuracies on the order of a few meters in real time.
Telescope
Astronomical satellites are satellites used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, and other outer space objects.
 The Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope Experimental
Tether satellites are satellites that are connected to another satellite by a thin cable called a tether. Recovery satellites are satellites that provide a recovery of reconnaissance, biological, space-production and other payloads from orbit to Earth. Biosatellites are satellites designed to carry living organisms, generally for scientific experimentation. Space-based solar power satellites are proposed satellites that would collect energy from sunlight and transmit it for use on Earth or other places.
Weapon
Since the mid-2000s, satellites have been hacked by militant organizations to broadcast propaganda and to pilfer classified information from military communication networks.[30][31] For testing purposes, satellites in low earth orbit have been destroyed by ballistic missiles launched from the Earth. Russia, United States, China and India have demonstrated the ability to eliminate satellites.[32] In 2007, the Chinese military shot down an aging weather satellite,[32] followed by the US Navy shooting down a defunct spy satellite in February 2008.[33] On 18 November 2015, after two failed attempts, Russia successfully carried out a flight test of an anti-satellite missile known as Nudol.[citation needed] On 27 March 2019, India shot down a live test satellite at 300 km altitude in 3 minutes, becoming the fourth country to have the capability to destroy live satellites.[34][35]
Pollution and interference
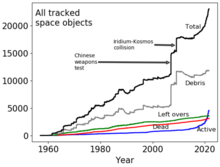 The growth of all tracked objects in space over time[36]
The growth of all tracked objects in space over time[36] Issues like space debris, radio and light pollution are increasing in magnitude and at the same time lack progress in national or international regulation.[37][36] Space debris pose dangers to the spacecraft[38][39] (including satellites)[39][40] in or crossing geocentric orbits and have the potential to drive a Kessler syndrome[41] which could potentially curtail humanity from conducting space endeavors in the future.[42][43]
With increase in the number of satellite constellations, like SpaceX Starlink, the astronomical community, such as the IAU, report that orbital pollution is getting increased significantly.[44][45][46][47][48] A report from the SATCON1 workshop in 2020 concluded that the effects of large satellite constellations can severely affect some astronomical research efforts and lists six ways to mitigate harm to astronomy.[49][50] The IAU is establishing a center (CPS) to coordinate or aggregate measures to mitigate such detrimental effects.[51][52][53]
Some notable satellite failures that polluted and dispersed radioactive materials are Kosmos 954, Kosmos 1402 and the Transit 5-BN-3.
Generally liability has been covered by the Liability Convention. Using wood as an alternative material has been posited in order to reduce pollution and debris from satellites that reenter the atmosphere.[54]
Due to the low received signal strength of satellite transmissions, they are prone to jamming by land-based transmitters. Such jamming is limited to the geographical area within the transmitter's range. GPS satellites are potential targets for jamming,[55][56] but satellite phone and television signals have also been subjected to jamming.[57][58]
Also, it is very easy to transmit a carrier radio signal to a geostationary satellite and thus interfere with the legitimate uses of the satellite's transponder. It is common for Earth stations to transmit at the wrong time or on the wrong frequency in commercial satellite space, and dual-illuminate the transponder, rendering the frequency unusable. Satellite operators now have sophisticated monitoring tools and methods that enable them to pinpoint the source of any carrier and manage the transponder space effectively.[citation needed]
You received this message because you are subscribed to the Google Groups "1top-oldtattoo-1" group.
To unsubscribe from this group and stop receiving emails from it, send an email to 1top-oldtattoo-1+unsubscribe@googlegroups.com.
To view this discussion on the web visit https://groups.google.com/d/msgid/1top-oldtattoo-1/CAGNPKmkrirKrFjB%3DF8vSUVj04EhpDmk-K0%3D2FcVmXf-DM_xLUQ%40mail.gmail.com.
No comments:
Post a Comment